Latest earthquakes near Japan today
Complete overview of the latest earthquakes near the country Japan, updated every minute. Did you feel an earthquake today in Japan? If an earthquake is happening right now near Japan (also known as 日本), it will show up within minutes.
Recent Japan Earthquake News
These are the latest articles published related to earthquakes occurring near Japan. Check our Earthquake News section for a complete overview of articles written on earthquakes near Japan and elsewhere.
Japan Earthquake Statistics
Average
A total of 10494 earthquakes with a magnitude of four or above have struck within 300 km (186 mi) of Japan in the past 10 years. This comes down to a yearly average of 1049 earthquakes per year, or 87 per month. On average an earthquake will hit near Japan roughly every 8 hours.
A relatively large number of earthquakes occurred near Japan in 2024. A total of 1563 earthquakes (mag 4+) were detected within 300 km of Japan that year. The strongest had a 7.5 magnitude.

Magnitude Distribution
The table below visualizes the distribution of all earthquakes that occurred within 300km of Japan in the past 10 years. No earthquakes with a magnitude of 8 or above have occurred near Japan during this time. Usually, higher magnitudes are less common than lower magnitudes. Small earthquakes with a magnitude below 4 on the Richter scale have been omitted from this overview.
| Magnitude | Earthquakes | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Mag. 4 | 9486 | 90.39% |
| Mag. 5 | 933 | 8.89% |
| Mag. 6 | 67 | 0.64% |
| Mag. 7 | 8 | 0.08% |
| Mag. 8 | 0 | 0.0% |
| Mag. 9 | 0 | 0.0% |
| Mag. 10 | 0 | 0.0% |
Strongest earthquakes near Japan
The strongest recent earthquake of the past 10 years near Japan occurred on Dec 8, 2025 23:15 local time (Asia/Tokyo timezone). It had a magnitude of 7.6 and struck 80 kilometers (50 mi) north-east of Hachinohe, at a depth of 45 km. Discover more strong earthquakes near Japan in the list below.
A longer time ago, a MAG-9.1 earthquake struck on Mar 11, 2011 14:46, 132 kilometers (82 mi) north-east of Sendai. It is the strongest earthquake near Japan in the past 126 years (Our data goes back to January 1st, 1900).
In the table below you will find the strongest earthquakes that occurred near Japan in the past 10 years. You can use the tabs to find the heaviest historic earthquakes since the year 1900 or within a specific year or distance from Japan.
Earthquakes by region of Japan
Click the links below for earthquake reports for regions in Japan.
- Aichi (愛知県)
- Akita (秋田県)
- Aomori (青森県)
- Chiba (千葉県)
- Ehime (愛媛県)
- Fukui (福井県)
- Fukuoka (福岡県)
- Fukushima (福島県)
- Gifu (岐阜県)
- Gunma (群馬県)
- Hirochima (広島県)
- Hokkaido (北海道)
- Hyōgo (兵庫県)
- Ibaraki (茨城県)
- Ishikawa (石川県)
- Iwate (岩手県)
- Kagawa (香川県)
- Kagoshima (鹿児島県)
- Kanagawa (神奈川県)
- Kumamoto (熊本県)
- Kyoto (京都府)
- Kōchi (高知県)
- Mie (三重県)
- Miyagi (宮城県)
- Miyazaki (宮崎県)
- Nagano (長野県)
- Nagasaki (長崎県)
- Nara (奈良県)
- Niigata (新潟県)
- Okayama (岡山県)
- Okinawa (沖繩縣)
- Saga (佐賀県)
- Saitama (埼玉県)
- Shiga (滋賀県)
- Shimane (島根県)
- Shizuoka (静岡県)
- Tochigi (栃木県)
- Tokushima (徳島県)
- Tokyo (東京都)
- Tottori (鳥取県)
- Toyama (富山県)
- Wakayama (和歌山県)
- Yamagata (山形県)
- Yamaguchi (山口県)
- Yamanashi (山梨県)
- Ōita (大分県)
- Ōsaka (大阪府)
Frequently Asked Questions
These questions are commonly asked in relation to earthquakes occurring near Japan.
When was the last earthquake in Japan?
A 4.4 magnitude earthquake hit near Japan on the morning of February 19, 2026 at 07:40 local time (Asia/Tokyo). The center of this earthquake was located 94km east-northeast of Iwaki at a depth of 30km under water in the North Pacific Ocean. Check the list on our website for any earthquakes occurring near Japan in the past hours.
What was the strongest earthquake near Japan?
A 9.1 magnitude earthquake hit near Japan on the afternoon of March 11, 2011 at 14:46 local time (Asia/Tokyo). The center of this earthquake was located 132km east of Sendai at a depth of 29km under water in the North Pacific Ocean. This is the strongest earthquake that occurred near Japan since the year 1900.
How often do earthquakes occur near Japan?
In the past 10 years, 10494 earthquakes with a magnitude of four or higher occurred within a 300 kilometer range from Japan. This averages to 1049 earthquakes yearly, or one earthquake every 8 hours.
 Feb 13, 2026 06:48AM
Shallow M5.5 Earthquake hit in the Philippine Sea 106km from Naha (Japan) on Friday Morning.
Feb 13, 2026 06:48AM
Shallow M5.5 Earthquake hit in the Philippine Sea 106km from Naha (Japan) on Friday Morning.
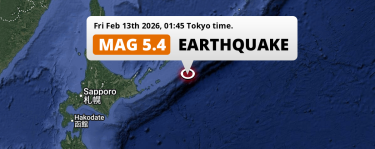 Feb 13, 2026 01:45AM
On Friday Night a Shallow M5.4 Earthquake struck in the North Pacific Ocean 273km from Nemuro (Japan).
Feb 13, 2026 01:45AM
On Friday Night a Shallow M5.4 Earthquake struck in the North Pacific Ocean 273km from Nemuro (Japan).
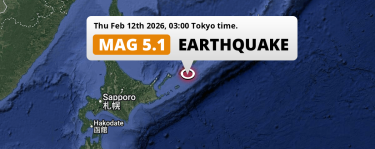 Feb 12, 2026 03:00AM
Significant M5.1 Earthquake hit in the North Pacific Ocean 290km from Kushiro (Japan) on Thursday Night.
Feb 12, 2026 03:00AM
Significant M5.1 Earthquake hit in the North Pacific Ocean 290km from Kushiro (Japan) on Thursday Night.
 Feb 5, 2026 03:20AM
Shallow M5.5 Earthquake hit in the Philippine Sea 273km from Kagoshima (Japan) on Thursday Night.
Feb 5, 2026 03:20AM
Shallow M5.5 Earthquake hit in the Philippine Sea 273km from Kagoshima (Japan) on Thursday Night.
 Jan 28, 2026 07:45PM
Shallow M5.1 Earthquake struck on Wednesday Evening in the North Pacific Ocean 135km from Hachinohe (Japan).
Jan 28, 2026 07:45PM
Shallow M5.1 Earthquake struck on Wednesday Evening in the North Pacific Ocean 135km from Hachinohe (Japan).
 Jan 22, 2026 11:31PM
Significant M5.3 AFTERSHOCK hit in the North Pacific Ocean 102km from Hachinohe (Japan) on Thursday Evening.
Jan 22, 2026 11:31PM
Significant M5.3 AFTERSHOCK hit in the North Pacific Ocean 102km from Hachinohe (Japan) on Thursday Evening.
