A significant M5.1 earthquake struck in the North Pacific Ocean 13 kilometer from Hitachi-Naka, Japan in the evening of Wednesday April 24th, 2024. The earthquake struck near a very densely populated region.
Felt the earthquake? Share this article: 



Earthquake Summary
This earthquake hit under water in the North Pacific Ocean, right off the coast of Japan (3 mi offshore), 13 kilometer east-northeast of Hitachi-Naka in Ibaraki. The center of this earthquake had a quite shallow depth of 55 km. Shallow earthquakes usually have a larger impact than earthquakes deep in the earth.
| Date and Time: | Apr 24, 2024 20:40 (Tokyo Time) - Apr 24, 2024 11:40 Universal Time. |
|---|---|
| Location: | 13 km ENE of Hitachi-Naka, Ibaraki, Japan. Coordinates 36°27'4"N 140°39'54"E. |
| Map: | 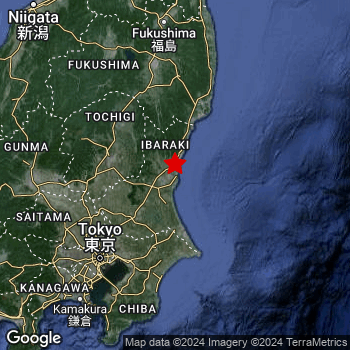 Map of area around epicenter. Click to open in Google Maps. |
| Magnitude: | MAG 5.1 Detected by 19 stations. Maximum Error Range ±0.071 . |
| Depth: | 55 km (34 mi) A quite shallow depth. |
| Tsunami Risk: | Low tsunami risk Earthquakes under MAG-6.5 do not usually cause tsunami's. Always stay cautious - More info here. |
Nearby towns and cities
This earthquake may have been felt in Japan . Funaishikawa in Ibaraki, Japan is the nearest significant place from the epicenter. The earthquake occurred 9 kilometer (6 mi) east of Funaishikawa.
Multiple major population centers exist within 300km of the earthquake that struck today. Tokyo is located 122 km to the southwest. Yokohama is located 145 km to the southwest. Hitachi-Naka is located 13 km to the west-southwest.
The table below provides an overview of all places in proximity of today's earthquake.
Overview of nearby places
| Distance | Place |
|---|---|
| 9 km (6 mi) W from epicenter |
Funaishikawa Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 13 km (8 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Hitachi-Naka Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 14 km (9 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Katsuta Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 17 km (11 mi) N from epicenter |
Hitachi Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 17 km (11 mi) SSW from epicenter |
Ōarai Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 22 km (14 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Mito Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 25 km (16 mi) WNW from epicenter |
Ōmiya Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 29 km (18 mi) SW from epicenter |
Okunoya Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 30 km (19 mi) N from epicenter |
Takahagi Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 35 km (22 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Tomobe Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 36 km (22 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Kasama Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 38 km (24 mi) N from epicenter |
Kitaibaraki Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 46 km (29 mi) SW from epicenter |
Ishioka Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 51 km (32 mi) W from epicenter |
Mashiko Tochigi, Japan. |
| 54 km (34 mi) S from epicenter |
Kashima-shi Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 58 km (36 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Tsukuba Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 58 km (36 mi) W from epicenter |
Mooka Tochigi, Japan. |
| 62 km (39 mi) SW from epicenter |
Ami Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 63 km (39 mi) SSW from epicenter |
Katori-shi Chiba, Japan. |
| 63 km (39 mi) SW from epicenter |
Naka Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 63 km (39 mi) SSW from epicenter |
Inashiki Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 63 km (39 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Shimodate Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 65 km (40 mi) SSW from epicenter |
Sawara Chiba, Japan. |
| 69 km (43 mi) NNE from epicenter |
Iwaki Fukushima, Japan. |
| 71 km (44 mi) W from epicenter |
Utsunomiya Tochigi, Japan. |
| 72 km (45 mi) SW from epicenter |
Ushiku Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 72 km (45 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Yūki Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 73 km (45 mi) NW from epicenter |
Ōtawara Tochigi, Japan. |
| 75 km (47 mi) SW from epicenter |
Ryūgasaki Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 79 km (49 mi) NW from epicenter |
Nasushiobara Tochigi, Japan. |
| 79 km (49 mi) NW from epicenter |
Kuroiso Tochigi, Japan. |
| 79 km (49 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Oyama Tochigi, Japan. |
| 80 km (50 mi) SW from epicenter |
Toride Ibaraki, Japan. |
| 81 km (50 mi) SSW from epicenter |
Narita Chiba, Japan. |
| 84 km (52 mi) W from epicenter |
Tochigi Tochigi, Japan. |
| 84 km (52 mi) W from epicenter |
Kanuma Tochigi, Japan. |
| 87 km (54 mi) SW from epicenter |
Abiko Chiba, Japan. |
| 90 km (56 mi) SSW from epicenter |
Sakura Chiba, Japan. |
| 90 km (56 mi) SW from epicenter |
Kashiwa Chiba, Japan. |
| 91 km (57 mi) SW from epicenter |
Noda Chiba, Japan. |
| 95 km (59 mi) SW from epicenter |
Nagareyama Chiba, Japan. |
| 97 km (60 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Kasukabe Saitama, Japan. |
| 100 km (62 mi) SW from epicenter |
Koshigaya Saitama, Japan. |
| 101 km (63 mi) SW from epicenter |
Matsudo Chiba, Japan. |
| 103 km (64 mi) SW from epicenter |
Honchō Chiba, Japan. |
| 107 km (66 mi) SSW from epicenter |
Chiba Chiba, Japan. |
| 109 km (68 mi) SW from epicenter |
Saitama Saitama, Japan. |
| 112 km (70 mi) SW from epicenter |
Kawaguchi Saitama, Japan. |
| 122 km (76 mi) SW from epicenter |
Tokyo Tokyo, Japan. |
| 134 km (83 mi) SW from epicenter |
Kawasaki Kanagawa, Japan. |
| 142 km (88 mi) W from epicenter |
Maebashi Gunma, Japan. |
| 145 km (90 mi) SW from epicenter |
Yokohama Kanagawa, Japan. |
| 200 km (124 mi) N from epicenter |
Yamagata Yamagata, Japan. |
| 203 km (126 mi) N from epicenter |
Sendai Miyagi, Japan. |
| 208 km (129 mi) WSW from epicenter |
Kōfu Yamanashi, Japan. |
| 217 km (135 mi) NW from epicenter |
Niigata Niigata, Japan. |
| 223 km (139 mi) W from epicenter |
Nagano Nagano, Japan. |
| 263 km (163 mi) SW from epicenter |
Shizuoka Shizuoka, Japan. |
| 277 km (172 mi) N from epicenter |
Ichinoseki Iwate, Japan. |
| 294 km (183 mi) W from epicenter |
Uozu Toyama, Japan. |
Shaking reported by 36 people
People that feel an earthquake may report their experience to the US Geographic Survey. Currently, 36 people have reported shaking in 16 places, all within Japan.We keep updating this article as more ground reports become available. You may report that you felt this earthquake here.
Places with most reports:
- Tokyo, Tokio, Japan: 20 people.
- Fussa, Chiba, Japan: 2 people.
- Kashiwa, Chiba, Japan: 1 person.
- Narita, Chiba, Japan: 1 person.
- Tomisato, Chiba, Japan: 1 person.
- Ōta, Gumma, Japan: 1 person.
- Naka, Ibaraki, Japan: 1 person.
- Yamato, Kanagawa, Japan: 1 person.
- Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan: 1 person.
- Yokosuka, Kanagawa, Japan: 1 person.
2 Aftershocks detected
Since this main shock, 2 smaller aftershocks were detected. Just 17 hrs after this main shock, an earthquake measuring MAG-4 was detected 8 km (5 mi) northwest of this earthquake.
Overview of foreshocks and aftershocks
| Classification | Magnitude | When | Where |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Shock This Earthquake |
M 5.1 |
Apr 24, 2024 20:40 (Tokyo Time) | - |
| Aftershock | M 3.7 |
36 mins later Apr 24, 2024 21:16 (Tokyo Time) | 8 km (5 mi) SW from Main Shock. |
| Aftershock | M 4.0 |
17 hrs later Apr 25, 2024 13:46 (Tokyo Time) | 8 km (5 mi) NW from Main Shock. |
More earthquakes coming?
The risk of aftershocks decreases rapidly over time. Usually, aftershocks are at least one order of magnitude lower than a main shock.
The chance that a significant earthquake like this one is followed by an even larger earthquake is not so large. On average, scientists estimate a 94% chance that a major earthquake will not be followed by an even larger one. It is still adviced to be aware of this risk
Read: How to Stay Safe during an Earthquake (cdc.gov).Earthquakes like this happen often in the region
Earthquakes of this strength are very common in the region. This is the strongest earthquake to hit since April 4th, 2024, when a 6.1 magnitude earthquake hit 175 km (109 mi) further north-east. An even stronger magnitude 7.3 earthquake struck on March 16th, 2022.
In total, 129 earthquakes with a magnitude of 5.1 or higher have been registered within 300km (186 mi) of this epicenter in the past 10 years. This comes down to an average of once every 28 days.
Low tsunami risk
Based on early data it appears this earthquake was not strong enough (lower than MAG-6.5) to be likely to cause destructive tsunami's. However this earthquake appeared to have hit at a shallow depth under sea, so stay cautious and monitor advice from local authorities.
Tsunami Risk Factors
| Factor | Under Sea? | MAG-6.5 or stronger? | Shallow depth? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Almost all tsunami's are caused by earthquakes with their epicenter under sea or very near the sea. However stay cautious in coastal areas as earthquakes on land may cause landslides into sea, potentially still causing a local tsunami. | Under MAG 6.5: Very unlikely to cause a tsunami. MAG 6.5 to 7.5: Destructive tsunami's do occur, but are uncommon. Likely to observe small sea level changes. MAG 7.6+: Earthquakes with these magnitudes might produce destructive tsunami's. |
Most destructive tsunami's are caused by shallow earthquakes with a depth between 0 and 100km under the surface of the earth. Deeper tsunami's are unlikely to displace to ocean floor. |
| This Earthquake | This earthquake appears to have struck under the sea. | Not this earthquake. This earthquake had a magnitude of 5.1. Earthquakes of this strength are unlikely to trigger a tsunami. |
This earthquake occurred at a depth of of 55 km (34 mi). Earthquakes this shallow could trigger a tsunami. |
Sources
Last updated 03/05/24 11:38 (). This article is automatically generated based on available data. We keep checking multiple sources for additional information. This article gets updated as new details on this earthquake become available.